General Understanding
Air conditioners work by removing heat and moisture from the air. As weather gets warmer, your air conditioner has to work alot harder. In the summer you can reduce solar heat gain by shading your home with awnings or trees on the eastern, southern, and western sides of the building. To keep your home from getting hot in the first place, reduce the amount of heat generated inside by efficient appliances, lights, etc. Make sure that windows are adequately sealed so that there are no leaks, and reduce solar radiation with window coverings. Adequate insulation in the rest of the house will help maintain a comfortable temperature. Make sure your unit is efficient; the higher the SEER rating, the more efficient the unit. We recommend a unit with a 12 SEER rating for more efficient energy use.
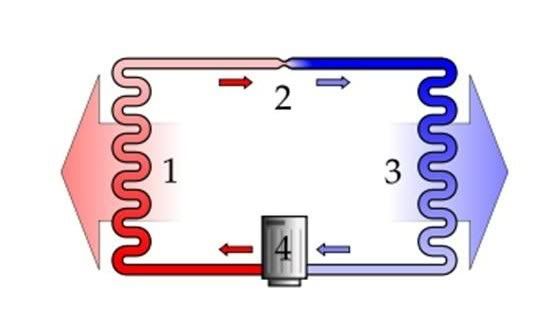
Evaporation Cycle
The outside unit which is called the Condenser compresses cool gas causing it to become hot high pressure gas. The high pressure gas now runs through the coils and turns into a liquid. The liquid then runs through an expansion valve to the inside of your house and evaporates to become a low pressure cold gas. The cold gas now runs through a set of coils that allows the gas to absorb heat and cool the air inside your house.
The outside unit which is called the Condenser compresses cool gas causing it to become hot high pressure gas. The high pressure gas now runs through the coils and turns into a liquid. The liquid then runs through an expansion valve to the inside of your house and evaporates to become a low pressure cold gas. The cold gas now runs through a set of coils that allows the gas to absorb heat and cool the air inside your house.
Energy Saving Ideas
Changing filters regularly, this will keep your blower from working hard also blower failure.
Check duct system for leaks.
Check refridgerant yearly, for proper levels. Errors in levels can reduce air conditioning efficiency 5% to 20% and increase energy costs.
Clean condersor yearly to prevent coils from clogging.
Choose size carefully. An oversized air conditioner can cause rooms to feel chilly, increase mold and mildew growth, and cost more. A small unit can turn on and off frequently, overworking the motor to try to cool a larger space inevitably resulting in burn out.
Set your thermostat to auto/cool. If it is set under 72, it will run all the time and increase your energy bill. If you are leaving for only a few hours, set your thermostat about 5-8 degrees higher than you usually have it. For every degree you raise your thermostat above 75 degrees you will save about 5 percent on your air conditioning bill. If you turn your unit off, any potential savings may be lost when you try to bring your temperature back to where you are comfortable.
How to check air flow
Supply air temperature and return temperature should have a 18 degree difference. If the air temperature is higher your refridgerant is under charged. If the air temperature is lower the refridgerant is over charged. This process will let you know if it is nescessary to call an A/C technician. The supply can be checked in your duct work above your indoor unit. Return can be checked in your return grill.
Tips
I cup of bleach poured monthly into your water lines will keep them running clearly.
Keep your Air conditioner set at the same temperature will save on your power bill.
Adding a return grill can cut down on loud noises.
Changing your filter montly. ( make a routine like when you pay your mortage or rent.)
At your local home improvement store you can rent equipment to blow recycled newspaper into your attic space right over existing insulation. This will help to cool your house and is also making your home more energy efficient. This may also increase the value of your home. This does not require any special licensing.
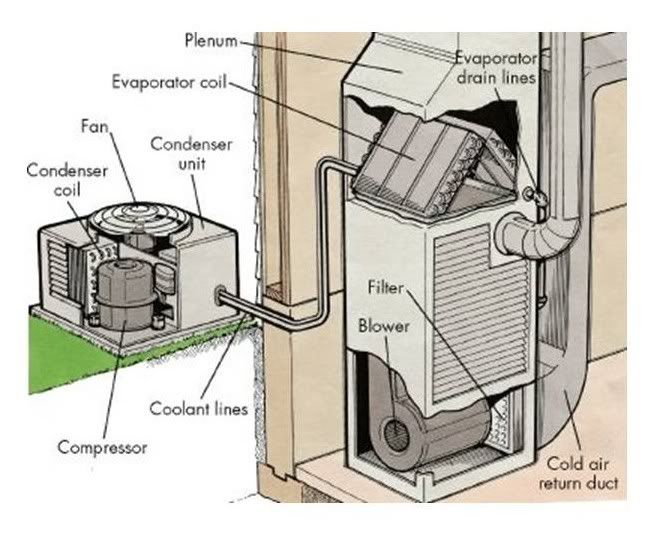
Basic Diagram of inside and outside unit
Air Conditioning Terms
· Condenser
· Coil
· Freon or Refrigerant
· Duct
· Fan
· Air Handler
· R-Value
· Cooling
· Heating
· Return grill
· Supply grills
· Filters
· Sequencer
· Blower motor
· Fan relays
· Disconnects
· Heating elements
· Compactor
· Contactors
· High and low voltage switch
· High and low pressure switch
· Compressor
· Thermostat
· Drain lines